
Oct. 30, 2018, 4:14 p.m.
KNOW YOUR BASIC RIGHTS...

The European Union, founded on democratic and rule of law principles, protects universal values such as human dignity, equality, justice, freedom and solidarity, has always made progress in developing the rights and freedoms that the individual has. While the Union contributes to the preservation and development of these values, it respects the different cultures and traditions of the European peoples and the national identities of the member states.
In the early years of the Union, even though there was no regulation on this issue in the primary sources, fundamental rights legislations emerged as a necessity within the union law which started to develop towards the end of the 60's. The Declaration of Conclusions of the Cologne Summit of 3-4 June 1999 concluded that these rights and freedoms should be clearly stated in the light of social and scientific progress in order to ensure the fundamental rights to be preserved and to protect the freedom of movement of goods, services and free movement of people in a regular and balanced manner. After signing the "European Union Charter of Fundamental Rights" in Nice in 2000, it was included in the primary legal sources through the Lisbon Treaty (2009).
With this Charter, the most basic rights were guaranteed including protection of human dignity, the right to life, the prohibition of torture and inhuman treatment, the right to physical-spiritual immunity of persons. As European law guaranteed individual rights of the people living in the member countries are regulated, the citizenship rights of the individuals are regulated in the Charter.

Source: https://twitter.com/eu_commission/status/733239474327572481
Every citizen in a member state within the Union (as in the local parliament) has the right to vote and run for the election of the European Parliament. Thus, the concept of "unity citizenship" has been developed with this condition. Having regard to the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union, the duties and authorities of the Union and the principle of subsidiarity,
• from their common constitutional values and international obligations,
• From European Union and Community agreements,
• From the European Convention on Human Rights,
• From social conditions accepted by the Community and the European Union,
• includes the rights of the European Court of Justice and the European Court of Human Rights arising from case law.
Charter of Fundamental Right: https://www.avrupa.info.tr/en/charter-fundamental-rights-european-union-708
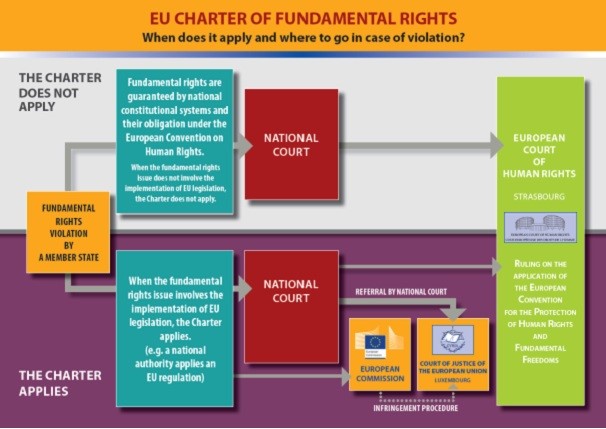
Image source: http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_MEMO-14-284_en.htm
Video Suggestion:

